2.To Kill a Mockingbird is a novel by Harper Lee published in 1960. It was immediately successful, winning the Pulitzer Prize, and has become a classic of modern American literature. The plot and characters are loosely based on the author's observations of her family and neighbors, as well as on an event that occurred near her hometown in 1936, when she was 10 years old.
The novel is renowned for its warmth and humor, despite dealing with the serious issues of rape and racial inequality. The narrator's father, Atticus Finch, has served as a moral hero for many readers and as a model of integrity for lawyers. One critic explains the novel's impact by writing, "In the twentieth century, To Kill a Mockingbird is probably the most widely read book dealing with race in America, and its protagonist, Atticus Finch, the most enduring fictional image of racial heroism."

Nelle Harper Lee (April 28, 1926 – February 19, 2016), better known by her pen name Harper Lee, was an American novelist widely known for To Kill a Mockingbird, published in 1960. Immediately successful, it won the 1961 Pulitzer Prize and has become a classic of modern American literature. Though Lee had only published this single book, in 2007 she was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom for her contribution to literature.
"I never expected any sort of success with Mockingbird. I was hoping for a quick and merciful death at the hands of the reviewers but, at the same time, I sort of hoped someone would like it enough to give me encouragement. Public encouragement. I hoped for a little, as I said, but I got rather a whole lot, and in some ways this was just about as frightening as the quick, merciful death I'd expected."
— Harper Lee, quoted in Newquist, 1964
3.Jude the Obscure, the last completed of Thomas Hardy's novels, began as a magazine serial in December 1894 and was first published in book form in 1895. Its protagonist, Jude Fawley, is a working-class young man, a stonemason, who dreams of becoming a scholar. The other main character is his cousin, Sue Bridehead, who is also his central love interest. The novel is concerned in particular with issues of class, education, religion and marriage.
The novel explores several social problems in Victorian England, especially those relating to the institutions of marriage, the Church, and education. These themes are developed in particular through Hardy's use of contrast. For example, at the beginning of their relationship, Jude's Christian faith contrasts with Sue's religious scepticism, a contrast which is heightened even further by their later role-reversal. Although the central characters represent both perspectives, the novel as a whole is firmly critical of Christianity and social institutions in general.
4.Tess of the d'Urbervilles: A Pure Woman Faithfully Presented is a novel by Thomas Hardy. It initially appeared in a censored and serialised version, published by the British illustrated newspaper The Graphic in and in book form in 1892. Though now considered a major nineteenth-century English novel and possibly Hardy's fictional masterpiece,Tess of the d'Urbervilles received mixed reviews when it first appeared, in part because it challenged the sexual morals of late Victorian England.
Thomas Hardy(2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, especially William Wordsworth.Charles Dickens was another important influence. Like Dickens, he was highly critical of much in Victorian society, though Hardy focused more on a declining rural society.
Most of his fictional works – initially published as serials in magazines – were set in the semi-fictional region of Wessex. They explored tragic characters struggling against their passions and social circumstances. Hardy's Wessex is based on the medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom and eventually came to include the counties of Dorset, Wiltshire, Somerset, Devon, Hampshire and much of Berkshire, in southwest and south central England.
5.Romeo And Juliet Act 2, scene 2

Romeo and Juliet is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare early in his career about two young star-crossed lovers whose deaths ultimately reconcile their feuding families. It was among Shakespeare's most popular plays during his lifetime , is one of his most frequently performed plays. Today, the title characters are regarded as archetypal young lovers.
Shakespeare's use of his poetic dramatic structure (especially effects such as switching between comedy and tragedy to heighten tension, his expansion of minor characters, and his use of sub-plots to embellish the story) has been praised as an early sign of his dramatic skill. The play ascribes different poetic forms to different characters, sometimes changing the form as the character develops. Romeo, for example, grows more adept at the sonnet over the course of the play.
 6.William Shakespeare (26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616)was an English poet, playwright, and actor, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet, and the "Bard of Avon".His extant works, including collaborations, consist of approximately 38 plays, 154 sonnets, two long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright.
6.William Shakespeare (26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616)was an English poet, playwright, and actor, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet, and the "Bard of Avon".His extant works, including collaborations, consist of approximately 38 plays, 154 sonnets, two long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright.
7.Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument in Wiltshire, England, 2 miles west of Amesbury and 8 miles north of Salisbury. Stonehenge's ring of standing stones are set within earthworks in the middle of the most dense complex of Neolithic and Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred burial mounds.
Archaeologists believe it was constructed from 3000 BC to 2000 BC. The surrounding circular earth bank and ditch, which constitute the earliest phase of the monument, have been dated to about 3100 BC. Radiocarbon dating suggests that the first bluestones were raised between 2400 and 2200 BC, although they may have been at the site as early as 3000 BC.
The site and its surroundings were added to UNESCO's list of World Heritage Sites in 1986 and it is a legally protected Scheduled Ancient Monument. Stonehenge is owned by the Crown and managed by English Heritage; the surrounding land is owned by the National Trust.
8.A Midsummer Night's Dream, a comedy believed to have been written by William Shakespeare between 1590 and 1597, portrays the events surrounding the marriage of Theseus, the Duke of Athens, to Hippolyta. These include the adventures of four young Athenian lovers and a group of six amateur actors (the mechanicals) who are controlled and manipulated by the fairies who inhabit the forest in which most of the play is set. The play is one of Shakespeare's most popular works for the stage and is widely performed across the world.
THESEUS (Act 5, scene 1)
More strange than true. I never may believe
These antique fables nor these fairy toys.
Lovers and madmen have such seething brains,
Such shaping fantasies, that apprehend
More than cool reason ever comprehends.
The lunatic, the lover, and the poet
Are of imagination all compact.
One sees more devils than vast hell can hold—
That is the madman. The lover, all as frantic,
Sees Helen’s beauty in a brow of Egypt.
The poet’s eye, in fine frenzy rolling,
Doth glance from heaven to Earth, from Earth to heaven.
And as imagination bodies forth
The forms of things unknown, the poet’s pen
Turns them to shapes and gives to airy nothing
A local habitation and a name.
Such tricks hath strong imagination,
That if it would but apprehend some joy,
It comprehends some bringer of that joy.
Or in the night, imagining some fear,
How easy is a bush supposed a bear!
9."Boys and Girls" (1964 / 1968) is a short story by Alice Munro, the Canadian winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2013 which deals with the making of gender roles.
Whenever she shares her daily routine farmwork with her father, the young narrator is taken to be a boy by visitors. She tries to keep away from any work in her mother's range of tasks because she does not really take any interest in that kind of work. The narrator remembers that by the time she was eleven years old she was faced with more and more expectations of what a girl should be like and what she should do or not do. Her role in the family began to change, and the narrator concludes with telling the story of an event in which she behaved according to her intuition, is squealed on by her younger brother and subsequently is being assigned the new gender role by her father. The narrator's last comment reads: ″Maybe it was true.″
Munro's fiction is most often set in her native Huron County in southwestern Ontario. Her stories explore human complexities in an uncomplicated prose style.Munro's writing has established her as "one of our greatest contemporary writers of fiction", including the 2013 Nobel Prize in Literature for her work as "master of the contemporary short story", She is also a three-time winner of Canada's Governor General's Award for fiction and was the recipient of the Writers' Trust of Canada's 1996 Marian Engel Award, as well as the 2004 Rogers Writers' Trust Fiction Prize for Runaway.
 10.Mimesis is a critical and philosophical term that carries a wide range of meanings, which include imitation, representation, mimicry, imitatio, receptivity, nonsensuous similarity, the act of resembling, the act of expression, and the presentation of the self.
10.Mimesis is a critical and philosophical term that carries a wide range of meanings, which include imitation, representation, mimicry, imitatio, receptivity, nonsensuous similarity, the act of resembling, the act of expression, and the presentation of the self.
Catharsis is the purification and purgation of emotions—especially pity and fear—through artor any extreme change in emotion that results in renewal and restoration.It is a metaphor originally used by Aristotle in the Poetics, comparing the effects of tragedy on the mind of spectator to the effect of a cathartic on the body
Hamartia , which means "to miss the mark" or "to err". It is most often associated with Greek tragedy, although it is also used in Christian theology.Hamartia as it pertains to dramatic literature was first used by Aristotle in his Poetics. In tragedy, hamartia is commonly understood to refer to the protagonist’s error or flaw that leads to a chain of plot actions culminating in a reversal from their good fortune to bad. What qualifies as the error or flaw can include an error resulting from ignorance, an error of judgement, a flaw in character, or sin.
 Aristotle ( 384–322 BC)was a Greek philosopher and scientist born in the city of Stagira, Chalkidice, on the northern periphery of Classical Greece. His father, Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, whereafter Proxenus of Atarneus became his guardian. At eighteen, he joined Plato's Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty-seven (c. 347 BC). His writings cover many subjects – including physics, biology, zoology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theater, music, rhetoric, linguistics, politics and government – and constitute the first comprehensive system of Western philosophy. Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request of Philip of Macedon, tutored Alexander the Great starting from 343 BC.According to the Encyclopædia Britannica, "Aristotle was the first genuine scientist in history ... every scientist is in his debt."
Aristotle ( 384–322 BC)was a Greek philosopher and scientist born in the city of Stagira, Chalkidice, on the northern periphery of Classical Greece. His father, Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, whereafter Proxenus of Atarneus became his guardian. At eighteen, he joined Plato's Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty-seven (c. 347 BC). His writings cover many subjects – including physics, biology, zoology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theater, music, rhetoric, linguistics, politics and government – and constitute the first comprehensive system of Western philosophy. Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request of Philip of Macedon, tutored Alexander the Great starting from 343 BC.According to the Encyclopædia Britannica, "Aristotle was the first genuine scientist in history ... every scientist is in his debt."Vocabulary
1.obs- perfix means "negative"
For Example- obscurity,obstacle
2. pri,prim-perfix means "first"
For Example-primary, prison
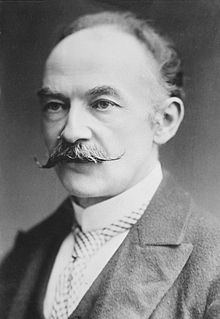


沒有留言:
張貼留言